Electric Ship Propulsion
The complete solution for electric ship propulsion consists of electric motors, scalable lithium-ion batteries with an energy management system, switch cabinets, bow thruster and propeller controls. The integrated automation systems, connected to all other subsystems via a bus system (such as CAN-bus), are used for the control and monitoring of the fully electric propulsion and auxiliary systems on board. The battery-electric propulsion system can be supplemented with one or two diesel emergency generators to ensure maneuverability even when the batteries are depleted (if legally required depending on the type of vessel).
Both AC and DC motors can be used. In the diagram below, a DC onboard power system is implemented with DC motors. The DC grid is powered by a battery pack that is charged via a DC charger connected to the shore power grid when the vessel is docked.
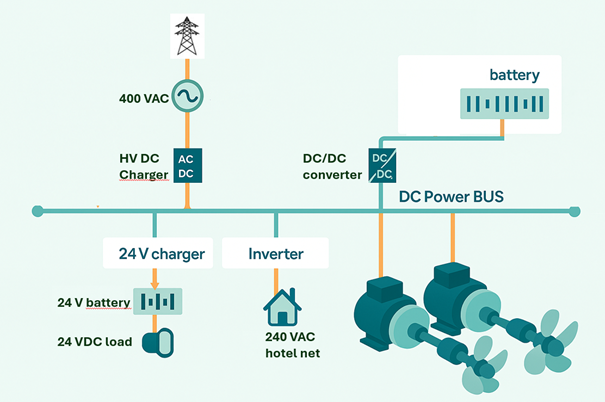
Block Diagram of Electric Ship Propulsion with DC Grid
The low-voltage onboard systems (navigation and communication systems) are powered by a separate 24V battery, which is charged from the DC grid via a 24V charger. The onboard 240 VAC hotel grid (for lighting and other amenities) is powered by an inverter connected to the DC grid.
For more information, please refer to the sections below.
1. Introduction to developments within the maritime industry
2. Electrically powered systems in the maritime industry
3. Standards and guidelines
5. Testing electric ship propulsion